Staying competitive in development businesses requires agility, scalability, and access to cutting-edge technologies. Many companies are realizing the limitations of on-premise infrastructure and turning to the cloud for a more efficient and cost-effective solution.
Microsoft Azure, a leading cloud platform, offers a suite of services designed to empower businesses of all sizes. However, migrating your existing IT environment to Azure can seem like a daunting task.
This comprehensive Microsoft Azure migration strategy step-by-step guide will equip you with the knowledge and strategies needed to navigate your Azure migration journey. We’ll break down the process into manageable stages, from initial planning to post-migration optimization.
What is Azure Migration?
Azure migration involves the process of transferring various IT assets, such as applications, databases, and server workloads, from an on-premises data center or another cloud platform (such as Amazon Web Services or Google Cloud) to Microsoft Azure.
The migration not only includes lifting and shifting physical servers to the cloud but also spans adapting applications for optimal cloud performance and security.
This strategic move is driven by the need to enhance business agility, reduce costs, and improve service delivery through Azure’s highly scalable and secure cloud infrastructure.
Major Benefits of Moving to Azure – Why It’s Worth To Move To Cloud?
Migrating to Azure not only simplifies infrastructure management but also introduces advanced capabilities that are difficult to achieve in traditional IT environments. Migrating to Azure provides transformative benefits, enabling businesses to adapt and scale efficiently.
Here are the top reasons why moving to Azure is beneficial:
- Cost Savings: Transitioning to Azure significantly reduces costs associated with on-premises servers, such as hardware ($1,000 to $4,000), software licensing ($500 to $4,000 for a Windows server), and maintenance ($200 to $900 for SQL Server). Azure’s pay-as-you-go model further helps by allowing payment only for the resources used, without upfront hardware investments.
- Increased Security and Compliance: Azure secures sensitive data with advanced 256-bit AES encryption, Multi-Factor Authentication, and comprehensive firewalls and identity management systems. It also complies with stringent standards necessary for regulated industries like healthcare and finance.
- Easy Integration and Scalability: Azure facilitates easy integration with existing systems, ensuring smooth transitions without downtime. Its scalable infrastructure adjusts to growing workload demands, ensuring continuous growth without technical limits.
- Improved Performance and Reliability: Hosted on remote servers managed by Microsoft, Azure reduces maintenance demands and enhances performance by minimizing latency. Its robust infrastructure ensures reliability and efficient handling of large-scale operations.
- Global Accessibility: Azure applications are accessible globally at any time, supporting seamless collaboration for remote teams and enabling operations beyond geographical limits.
By optimizing technological resources and aligning with modern IT practices, Azure drives dynamic growth, enhanced security, and operational efficiency, making it an excellent choice for forward-thinking businesses.
Planning Your Successful Azure Migration – What To Consider Before?
A successful Azure migration requires a structured approach and careful planning. Before diving into the migration process, it’s crucial to assess your existing IT environment, set clear migration goals, and choose a migration strategy that aligns with your business needs.
This strategic foundation will not only streamline the transition but also maximize the benefits of Azure for your organization.
-
Understanding Your IT Landscape (Current Infrastructure Assessment)
Begin by conducting a thorough assessment of your current IT landscape. This step involves:
- Inventory Creation: Compile a detailed inventory of all your IT assets, including servers, applications, and data systems.
- Dependency Mapping: Develop a map of how these assets interact and depend on each other. This will help identify potential challenges in the migration process, such as application dependencies that could affect functionality if not properly managed.
- Performance Baseline: Establish a performance baseline of your systems to help evaluate the effectiveness of the migration in terms of speed and resource utilization.
- Engaging stakeholders: Involve your IT and business teams from the outset. Their input ensures alignment with business goals and minimizes disruption.
This comprehensive assessment will provide a clear picture of your infrastructure and is critical for planning a successful migration.
-
Defining Your Azure Migration Goals (Cost Savings, Scalability, etc.)
Defining clear migration plan goals is crucial. Consider what your organization aims to achieve with Azure migration. Common goals include:
- Cost Reduction: Analyze current expenses to see where moving to Azure can save money.
- Improved Scalability: Determine how cloud scalability can address business growth or variable demand.
- Enhanced Performance: Identify performance bottlenecks in your current setup that Azure could improve.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure Azure’s capabilities align with industry-specific regulatory requirements.
Align these goals with overall business objectives to ensure that the migration supports your company’s strategic direction.
-
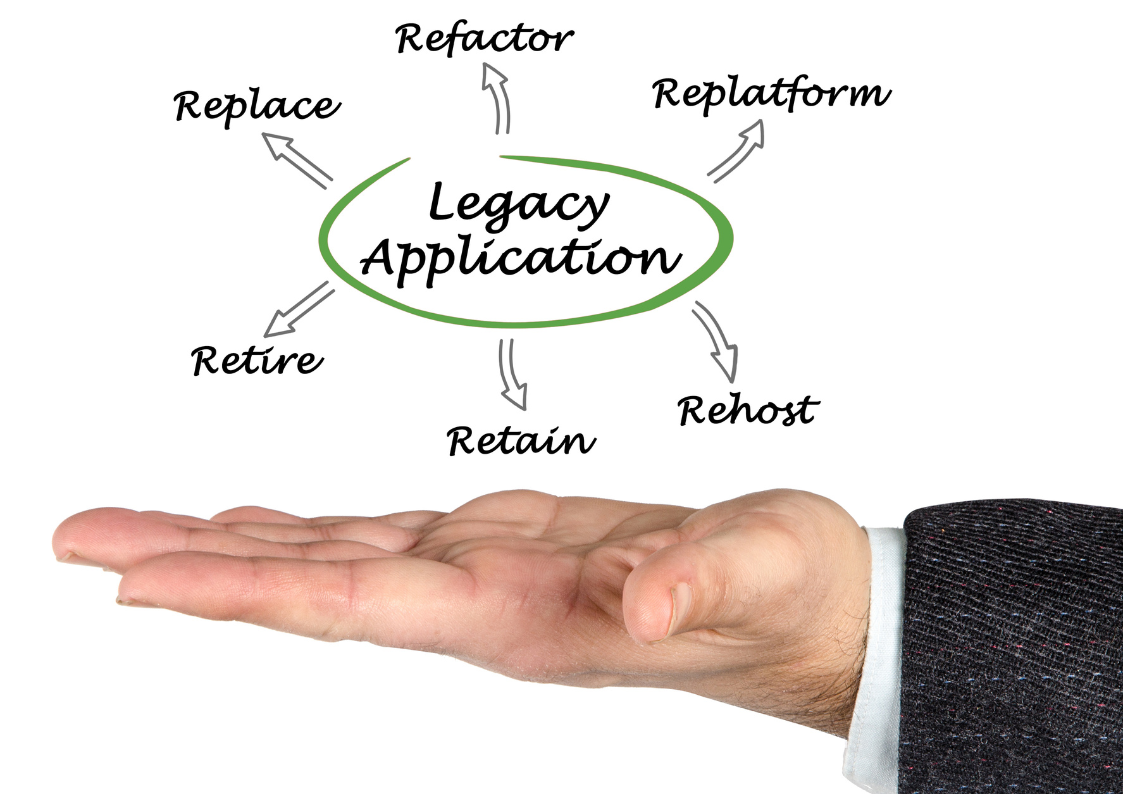
Choosing the Right Azure Migration Strategy (Lift-and-Shift, Refactoring, etc.)
Selecting the right migration strategy is vital for a smooth transition:
- Lift-and-Shift (Rehost): This approach involves moving applications and data to Azure with no or minimal changes. It is quick and cost-effective for applications that are suitable for the cloud as-is.
- Refactor: This strategy involves making minor adjustments to applications to optimize their performance in the cloud. It’s beneficial for improving scalability and cost-efficiency.
- Re-architect: In some cases, significant modifications are necessary to make applications cloud-native. This might include adopting microservices architecture or leveraging serverless computing.
- Rebuild or Replace: Sometimes, it is more cost-effective to completely rebuild an application using cloud-native technologies or replace it with a third-party software as a service (SaaS) solution.
Each strategy has different implications for cost, time, and resource requirements. The choice should be based on a detailed analysis of your current infrastructure, application architecture, and business needs.
Developing Your Microsoft Azure Migration Action Plan – Step-by-Step Guide
Developing a smart migration to Azure strategy that minimizes downtime and ensures a smooth transition is crucial for the successful adoption of Azure cloud services. This section will discuss how to effectively plan and execute an Azure migration tailored to meet specific business needs, providing a comprehensive action plan.
Inventorying and Prioritizing Workloads for Migration
The first step in your Azure migration plan involves inventorying your existing IT assets and prioritizing which workloads to migrate based on their importance, complexity, and the business value they deliver. This process should include:
- Assessing Each Workload: Evaluate how each workload operates, its requirements, and its importance to your business operations.
- Prioritization: Decide the order of migration based on factors such as workload interdependencies, business criticality, and readiness for migration. Start with less critical systems to mitigate risk.
Selecting the Most Effective Azure Migration Tools (Azure Migrate, Azure Data Box, etc.)
Choosing the right tools is essential for a smooth migration. Microsoft offers several tools designed to facilitate different aspects of the Azure migration process:
- Azure Migrate: Provides a central hub for the assessment and migration of on-premises servers, databases, applications, and more.
- Azure Data Box: Useful for offline data transfer when migrating large amounts of data to Azure.
- Azure Database Migration Service: Streamlines the process of migrating databases to Azure and manages schema and data migration.
Phased Cloud Migration vs. Big Bang Migration
Decide between a phased migration and a big bang approach:
- Phased Migration: Involves migrating services and applications in stages. This approach reduces risk by allowing adjustments and resolving issues in earlier phases before full-scale deployment.
- Big Bang Migration: All components are migrated in a single, comprehensive move. This method is faster but carries higher risk and potential for significant downtime.
The choice depends on your organization’s risk tolerance, the complexity of the IT environment, and resource availability.
| Aspect | Phased Migration | Big Bang Migration |
| Description | Migrating services and applications in stages. | Migrating all components in a single, comprehensive move. |
| Risk Level | Lower risk, as it allows for adjustments and issue resolution in earlier phases. | Higher risk, due to the simultaneous migration of all components. |
| Downtime | Minimal and managed downtime, as only parts of the system are moved at any one time. | Potential for significant downtime, as the entire system is migrated at once. |
| Speed | Slower, as the migration is spread out over multiple stages. | Faster, as everything is migrated at once. |
| Complexity Management | Easier to manage complexity, as each phase can be planned and executed with a focus on specific components. | More complex to manage, as it involves the entire system’s migration at once. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility in managing and addressing issues as they arise during earlier phases. | Less flexibility, as all issues must be handled simultaneously post-migration. |
| Suitability | Suitable for complex environments with interdependent systems that require careful coordination. | Suitable for smaller, less complex environments or when speed is a critical factor. |
Setting Up Your Azure Subscription and Resource Creation
Before migrating, set up your Azure subscription and configure the necessary Azure resources. This step involves:
- Subscription and Resource Group Setup: Organize resources in logically grouped collections to simplify management and billing.
- Resource Deployment: Deploy virtual networks, storage accounts, and other foundational elements that your workloads will require in Azure.
Migration Process Breakdown (Data Migration, VM Migration, Application Migration)
The actual migration involves several key processes:
- Data Migration: Move data securely using tools like Azure Data Box or Azure Import/Export service.
- VM Migration: Use Azure Migrate to move virtual machines from VMware or on-premises servers to Azure.
- Application Migration: Re-host applications using Azure Virtual Machines or refactor them to run on Azure App Services.
- Azure SQL Database: Before migration, assess your current database systems for compatibility with Azure SQL Database. Tools like the Data Migration Assistant (DMA) can help identify potential issues with database features that might not be supported in Azure.
Each type of migration requires specific planning to address the unique challenges involved.
Testing and Validation for a Secure and Error-Free Migration
After migrating, thoroughly test and validate each component to ensure it functions as expected in the new environment. This phase should include:
- Performance Testing: Check that the migrated applications meet performance criteria.
- Security Validation: Ensure all security measures are correctly configured and that data integrity is maintained.
- User Acceptance Testing: Confirm that end users can interact with the migrated applications without issues.
This comprehensive testing and validation ensure that your Azure environment is optimized, secure, and fully operational.
Optimizing Your Azure Cloud Environment For Post-Migration Success
Once your Azure migration is complete, the next critical phase is to optimize your cloud environment to ensure ongoing operational efficiency and security. This involves monitoring performance, managing resources, securing your setup, and integrating continuous processes for improvement.
-
Performance Monitoring and Resource Management in Azure
Effective performance monitoring and resource management are crucial for maintaining an optimized Azure environment. Here’s how you can achieve this:
- Azure Monitor: Use Azure Monitor to track performance and health metrics across all Azure services. It provides comprehensive capabilities to collect, analyze, and act on telemetry data from your Azure and on-premises environments. Set up dashboards to visualize metrics and gain insights into your applications and infrastructure.
- Resource Sizing and Scaling: Regularly review performance data to right-size Azure resources, ensuring you are using the optimal service tier and scale. Azure’s consumption-based model allows for dynamic resizing, which you can manage through the Azure portal, PowerShell, or Azure CLI.
- Cost Management: Azure Cost Management tools help track resource usage and manage costs effectively. Implement cost analysis, set up budget alerts, and create policies to control spending. This helps in aligning resource utilization with budget constraints and operational needs.
- Azure Advisor: Leverage Azure Advisor to get personalized recommendations on how to improve efficiency by reducing costs and optimizing Azure deployments. It analyzes your resource configuration and usage to provide best practices for effectively managing your Azure environment.
-
Security Best Practices for Your Azure Cloud Environment
Securing your Azure environment is crucial for protecting data and maintaining compliance with industry standards. Implement these security best practices:
- Azure Security Center: Utilize Azure Security Center for unified security management and advanced threat protection across all of your Azure resources. It helps in strengthening security posture, protecting against threats, and getting secure score recommendations.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Ensure that Azure Multi-Factor Authentication and Role-Based Access Control are configured to enhance security protocols and manage access permissions efficiently.
- Azure Sentinel: Set up Azure Sentinel, a scalable, cloud-native, security information event management (SIEM) and security orchestration automated response (SOAR) solution. It provides intelligent security analytics and threat intelligence across the enterprise, offering a single solution for alert detection, threat visibility, proactive hunting, and threat response.
-
Continuous Integration and Delivery (CI/CD) for Ongoing Management
Integrating CI/CD pipelines within your Azure environment facilitates ongoing management and ensures continuous improvement:
- Azure DevOps: Utilize Azure DevOps for managing CI/CD pipelines that automate the building, testing, and deployment of your applications within Azure. This supports a rapid and secure development lifecycle.
- Automated Testing and Deployment: Implement automated testing to validate code and configuration changes, followed by automated deployment to streamline release processes and reduce human errors.
- Monitoring and Feedback Loops: Establish monitoring within your CI/CD pipelines to gather feedback from production operations. Use this data to continuously improve application performance and user experience.
By adopting these optimization strategies, you can ensure that your Azure environment remains efficient, secure, and aligned with your business objectives, thus maximizing the benefits of your cloud investment.
Best Practices for a Successful Azure Migration
A successful Azure Cloud migration requires a focus on security, compliance, and cost optimization.
Here’s how to make it happen:
- Security First: Integrate security throughout the process. Leverage Azure’s built-in features like RBAC and encryption to safeguard your data. Conduct regular security testing and maintain compliance with relevant regulations.
- Cost Optimization: Right-size your resources and leverage Azure’s cost management tools like cost analysis and budgets. Continuously monitor and optimize resource utilization to avoid unnecessary spending.
- Phased & Tested Migration: For complex environments, consider a phased migration to minimize disruption. Pilot and rigorously test workloads before migrating critical applications.
- Communication & Training: Maintain clear communication with stakeholders and invest in training your IT staff on Azure best practices.
By following these practices, you ensure a secure, compliant, and cost-effective migration, setting the stage for a successful journey to the cloud.
Common Challenges and Solutions While Migrating Projects To Azure
Migrating to Microsoft Azure offers substantial benefits for businesses seeking to enhance their infrastructure and operations.
However, the transition can introduce a range of challenges that need careful consideration and strategic planning to overcome. Below, we discuss some common issues encountered during Azure migration and provide practical solutions and troubleshooting tips.
Handling Data Loss and Downtime
Challenge: Data loss and system downtime are among the most critical concerns during cloud migration. These issues can disrupt business operations and lead to significant financial and reputational damage.
Solutions:
- Robust Backup and Recovery Plans: Implement comprehensive data backup procedures before beginning the migration. Azure’s own backup services can be configured to ensure that all critical data is recoverable in the event of an error.
- Incremental Migration: Instead of migrating all data at once, consider incremental migration approaches that minimize the volume of data moved at any one time, thereby reducing the risk of data loss.
- Thorough Testing: Before going live, conduct extensive testing to ensure that data integrity is maintained throughout the migration process. Use Azure’s data migration tools that include validation steps to check data completeness and accuracy.
Technical Challenges and Their Resolutions
Challenge: Technical issues can range from compatibility problems with existing applications to difficulties in estimating the required resources, leading to either overutilization or wasteful expenditure.
Solutions:
- Compatibility Assessments: Early in the migration planning process, perform detailed assessments of your existing applications to identify potential compatibility issues. Tools like Azure Migrate can help evaluate and mitigate compatibility problems by providing insights and recommendations.
- Resource and Cost Management: Utilize Azure’s pricing calculator to better estimate the costs associated with the migration and ongoing expenses. Adopt Azure Cost Management and Azure Advisor to monitor and optimize resource usage to prevent overspending.
- Application Refactoring: Some legacy applications may not be optimized for a cloud environment and may require refactoring or even complete rewriting. Plan for this by setting aside resources and time, and consider using Azure App Service or Azure Kubernetes Service to modernize applications.
- Access Control and Security: To tackle security concerns, implement stringent access controls using Azure Active Directory and role-based access controls (RBAC). Regularly review and update these policies to protect against unauthorized access and potential cyber threats.
Conclusion – Should You Look Into Professional Microsoft Azure Migration Services?
Migrating to Microsoft Azure represents a strategic decision that can significantly enhance your organization’s scalability, flexibility, and efficiency. Throughout this guide, we’ve explored the step-by-step process of Azure migration, highlighting the major benefits.
We’ve also discussed the critical planning stages, including assessing your IT landscape, defining migration goals, and selecting the right migration strategy.
For many organizations, especially those with limited in-house expertise in cloud migrations, professional Azure migration services offer a valuable advantage. These services can help you navigate the complexities of the migration process, from initial planning and execution to optimization and ongoing management.
Multishoring, with its deep expertise in Microsoft Azure services and development project migrations, is perfectly equipped to provide the guidance and support necessary to ensure your migration is successful. Our professionals are adept at crafting personalized migration strategies that minimize downtime, enhance security, and optimize performance.
Our Azure Development, Migration and Consulting Services
Let's talk about your IT needs

Let me be your single point of contact and lead you through the cooperation process.
Choose your conversation starter
Signed, sealed, delivered!
Await our messenger pigeon with possible dates for the meet-up.